| Package Data | |
|---|---|
| Maintainer Username: | brynj-digital |
| Maintainer Contact: | contact@gbrock.com (Greg Brock) |
| Package Create Date: | 2017-08-16 |
| Package Last Update: | 2018-03-27 |
| Home Page: | |
| Language: | PHP |
| License: | MIT |
| Last Refreshed: | 2026-03-04 03:22:58 |
| Package Statistics | |
|---|---|
| Total Downloads: | 356 |
| Monthly Downloads: | 0 |
| Daily Downloads: | 0 |
| Total Stars: | 3 |
| Total Watchers: | 1 |
| Total Forks: | 1 |
| Total Open Issues: | 0 |
This package contains flexible ways of rendering Eloquent collections as dynamic HTML tables. This includes techniques for sortable columns, customizable cell data, automatic pagination, ~~user-definable rows-per-page, batch action handling, and extensible filtering~~ (coming soon).
Require the package in your composer.json:
"gbrock/laravel-table": "dev-master"
Add the service provider to config/app.php and, optionally, the Facade:
'Gbrock\Table\Providers\TableServiceProvider',
...
'Table' => 'Gbrock\Table\Facades\Table',
Publish the views and config:
php artisan vendor:publish
In order to render an HTML table of Eloquent models into a view, first create a Table object, passing in your model collection (this could be done in your controller, repository, or any service class):
$rows = User::get(); // Get all users from the database
$table = Table::create($rows); // Generate a Table based on these "rows"
Then pass that object to your view:
return view('users.index', ['table' => $table]);
In your view, the table object can be rendered using its render function:
{!! $table->render() !!}
Which would render something like this:
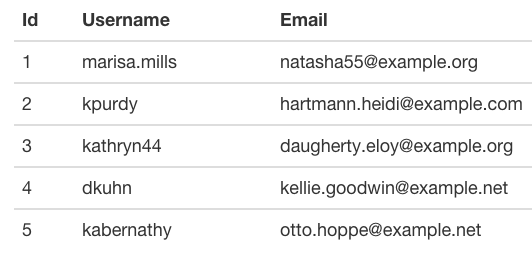
To add links in your headers which sort the indicated column, add the Sortable trait to your model. Since no
fields are allowed to be sorted by default (for security reasons), also add a sortable array containing allowed fields.
use Gbrock\Table\Traits\Sortable;
class User extends Model {
use Sortable;
/**
* The attributes which may be used for sorting dynamically.
*
* @var array
*/
protected $sortable = ['username', 'email', 'created_at'];
This adds the sortable scope to your model, which you should use when retrieving rows. Altering our example,
$rows = User::get() becomes:
$rows = User::sorted()->get(); // Get all users from the database, but listen to the user Request and sort accordingly
Now, our table will be rendered with links in the header:

The links will contain query strings like ?sort=username&direction=asc.
If you paginate your Eloquent collection, it will automatically be rendered below the table:
$rows = User::sorted()->paginate(); // Get all users from the database, sort, and paginate
Pass in a second argument to your database call / Table creation, columns:
$table = Table::create($rows, ['username', 'created_at']); // Generate a Table based on these "rows"
You can specify a closure to use when rendering cell data when adding the column:
// We pass in the field, label, and a callback accepting the model data of the row it's currently rendering
$table->addColumn('created_at', 'Added', function($model) {
return $model->created_at->diffForHumans();
});
Also, since the table is accessing our model's attributes, we can add or modify any column key we'd like by using accessors:
protected function getRenderedCreatedAtAttribute()
{
// We access the following diff string with "$model->rendered_created_at"
return $this->created_at->diffForHumans();
}
The default view favors the rendered_foobar attribute, if present, otherwise it uses the foobar attribute.
A copy of the view file is located in /resources/vendor/gbrock/tables/ after you've run php artisan vendor:publish.
You can copy this file wherever you'd like and alter it, then tell your table to use the new view:
$table->setView('users.table');